According to GSMA, The Mobile Economy 2018 report, 4G will become leading mobile network technology having more than 3 billion connection while the industry continues to grow with 5G in 2019. 4G is the fourth generation of broadband cellular network launched in late 2009 with a motive to provide more data speed and security. 4G provides speed up to ten times higher than of Turbo-3G, or 80 Mbit/s in optimal conditions. 4G is based on the LTE technology (Long Time Evolution), an international standard and a complete IP based technology for data transmission. While 5G is the latest generation succeeding 4G which offers faster speed than current connections, with average download speeds of around 1GBps.
Recently, three new vulnerabilities have been discovered in both 4G and 5G which allowed interception of calls and tracking mobile location.
4G and 5G Vulnerability
4G and 5G are known to provide better speed and security especially against law enforcement use of cell site simulators named “stingrays”. Stringray is a IMSI catcher which allowed LEAs to locate people using their phone’s location. However, researchers have found new security flaws that affect both 4G and 5G.
The academic researchers at the Network and Distributed System Security Symposium in San Diego on Tuesday published a research paper highlighting the 4G and 5G vulnerability . Although due to the potential of attack, researchers did not release any proof of concept to avoid exploitation of vulnerabilities. As the fix of this vulnerability is not straight forward and just like SS7 Exploitation requires a patch at core network equipment , but even if the PoC has not been shared it is a matter of time before we will be seeing the exploit open in the first, first they might be sold on the dark market later seen at every other hacking forum, As Hussain who was a researcher at Network and Distributed System Security Symposium said
Any person with a little knowledge of cellular paging protocols can carry out this attack… such as phone call interception, location tracking, or targeted phishing attacks.
Discovery of 4G / 5G Vulnerability
Mobiles go into idle condition to conserve energy when there is no active connection with a base station. Paging protocol is used to notify a device for an incoming call or a message. For more than one or more pending service, Mobile Management Entity (MME) ask base station(s) to broadcast a paging message, which includes the Temporary Mobile Subscriber Identity (TMSI) of the phone and assigned randomly by MME.
Using random, unpredictable values for new TMSI protect against sniffing attacks. However, researchers managed to bypass this natural defense system which is explained below.
ToREPDO on 4G/5G
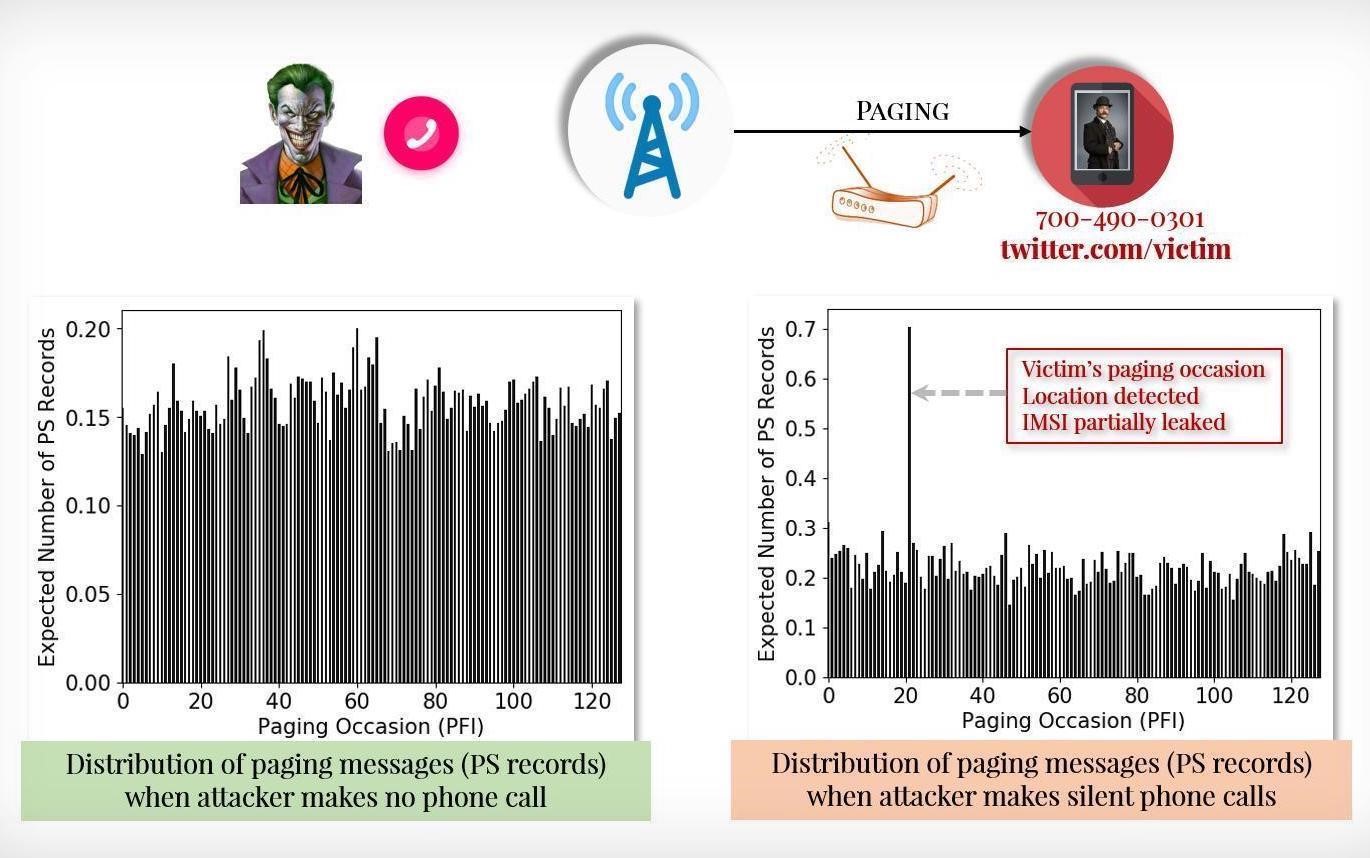

ToRPEDO applies to both 4G and 5G and exploits paging protocol by making frequent phone calls in a short time which triggers a paging message without alerting the victim’s device and unveil the victim’s location. The attacker can hijack the paging channel and run a denial of services attack by injecting or denying paging messages. With ToRPEDO, the attacker can also inject spoofing messaging such as Amber alerts.
PIERCER on 4G
ToRPEDO vulnerability gives an opportunity for PIERCER (Persistent Information ExposuRe by the CorE netwoRk) attack which will reveal the victim’s phone number international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) on the 4G network. PIERCER makes it easy to further attack the victim by exposing ISMI.
IMSI-Cracking on 4G/5G
ToRPEDO also gives an opportunity for IMSI Cracking attack on both 4G and 5G using the victims’ phone number and brute-forcing. According to researchers, for US subscribers, it takes around 13 hours to guess the victim’s IMSI with a brute-force attack and two oracles (one for 4G and another for 5G) designed by researchers.
Conclusion
According to authors, 3 Canadian and all US carriers are vulnerable to ToRPEDO, while PIERCER is verified on one major carrier of US and three major carriers of South Asian countries,Hussain further explained it:
Almost all the cell networks outside the U.S. are vulnerable to these attacks, several networks in Europe and Asia are also vulnerable
The paper also covers the defense mechanism for these vulnerabilities pointing towards ToRPEDO as the major cause of exploit. The authors have designed a countermeasure which adds noise in the form of a fake paging message for perturbing the underlying paging message distribution, But it is easier said then done.
Does 5G come with faster speed and better security by mitigating new vulnerabilities?









[…] . Supply hyperlink […]
[…] New Network Vulnerabilities can Hack 4G and 5G […]