Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain have shown potential in providing various methods for threat detection, while both differ in nature, the combination of the two or even standalone capabilities can be of great help in cyber security. Cybersecurity is of utmost importance because in this era of digitization latest attack vectors need to be warded off. This article will go in-depth showing how Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence can be used for averting cyber threats. If you want to learn how bad actors work, what is done with your information and how threats can be eliminated you must attend the Cyber Security For Defense Conference where experts talk about the ‘latest’ and upcoming developments and requirements in Cybersecurity (Discount coupon is shared at the end of article).
AI and Blockchain in Cybersecurity Threat Detection
Cyber attacks are constantly evolving to breach into our networks successfully, as reported in “2018 SonicWall Cyber Threat Report”
there is an increase in cyber attacks and malware variants by 101.2%. Cyber criminals are moving to highly effective tools to target companies around the globe. 62% of IT leaders in Europe consider data security a key investment priority.
A study conducted by an IBM and Ponemon Institute showed an increase of global data breach cost by 6.4% in year 2018. With the increase in online data for organizational operations, the cost of any security breach also increases.
There is growth in the use of IoT which increases the risk for organizations and the need for data protection policies. Organizations are not taking enough steps to secure themselves from cyber attacks; ultimately, there will be an increase in attack size and volume.
Recent Cyber Threats
Trends in malware variants and mobile security have been outlined in Symantec’s annual Internet Security Threat Report. Researchers have found that new malware for Mac computers has risen by 80%, and mobile variants have increased by 54%. 5.4 billion cases of thwarted Wannacry attacks have been documented in the report.
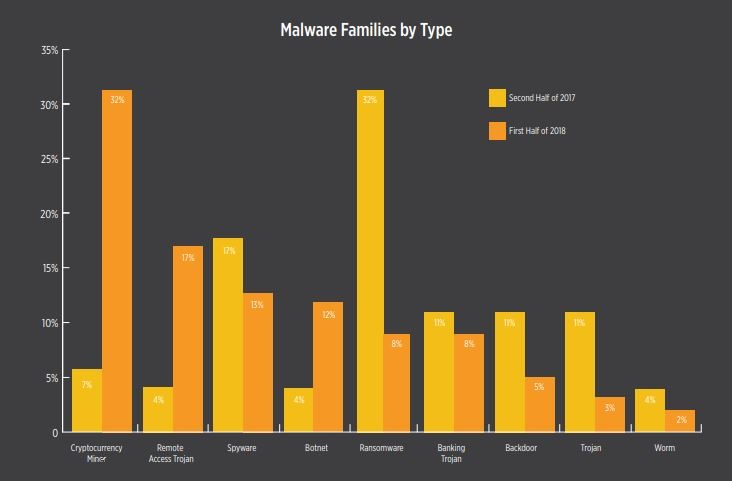
Like several threat researches, Symantec has also found a major increase in coin mining attacks. The increase was probably the result of the Cryptocurrency boom last winter, but with increased coin value, mining attacks increased. Cryptomining attacks virtually did not exist some years back. However, according to Skybox Security’s Vulnerability and Threat trends 2018, there has been an increase from around 7% of the 2017 malware variants to more than 30% through the first half of 2018.

The latest significant change in cyber threats concerns ‘fraud’ in social media. According to Proofpoint’s Social Media brand fraud report, social media fraud grew by 200% between the fourth quarter of 2017 and the first quarter of 2018. Cyber crimes are using ‘bait’ like email telephone tactics to infect corporate and personal social accounts. You can build a fraudulent brand page and offer discounted services, customer support or benefits. They will then send users to websites that request personal data or have malicious download links.
Artificial Intelligence in Cyber Security
Nowadays, almost all cyber security products seem to be using artificial intelligence. You may realize that some experts discuss a breakthrough while others push the hype further. Although this issue is already hot in public speaks, almost every security expert considers that AI can solve the current challenges in the cyber security sector. On the other hand, hackers benefit from new AI approaches and the key question at this stage is how important the potentials and consequences of this new technology are.
Why we need AI in Cyber security
You can see that many companies have invested a lot to gain more value from their architecture and security operations centers when examining the security architecture. Companies still have difficulties protecting their enterprises and data, this is because internal processes and security teams are constrained by technological restrictions that are compounded by the sophistication of the attacks.
Consequently, the technological restrictions and processes need to be overcome so that SOC teams can stay ahead of the most advanced attacks. Disparate tools must be integrated into the common security architecture and AI processes of investigation and response can be achieved by improved performance, accuracy, and handling of large data-sets.
Also, we have reached the limits of signatures and heuristics because of a dramatic increase of new and unknown malware every day, the total number of malware players and the size of Darknet. Signatures represent the malicious code’s fingerprint and aid in detecting and identifying malware. One of the weaknesses of this approach is that simple modifications of malware features often bypass signatures detection. Some experts say anti-virus signatures now only cover 30-40% of malware, although others think it can be as high as 65%, yet a great percent is left which can be very harmful for an organization.
Malware Detection using AI
A sandboxing solution for identifying malware or malicious domains must be used to train the engine with predefined, labeled data. The algorithm extracts relevant features, gives them the importance and can then predict if the input file is malware or benign according to a percentage value as shown in the table.
| Extracted Feature | Good documents | Malicious documents |
| Document name | 0.9% | 84.4% |
| No title | 6.6% | 50.2% |
| Obfuscated function calls | 0.1% | 39.6% |
| Accesses host file | 21.8% | 49.5% |
| DNS resolution | 27.4% | 50.4% |
| Excessive sleep calls | 43.6% | 67.1% |
Deep Learning for Security Operation Centers
The most important use case is the use of DL as a model for threat identification and investigation in the Security Operation Center, which is expected to be a fundamental future approach for cyber security space. The lack of skills in the security market and manual processes exacerbates this problem. To identify slow-moving attacks, detection model also must have long-term memory to keep the context of related activities over time.
A radical thesis is to replace legate approaches based on DPI by security models that extract metadata through network sensors that are supported by other system logs and enrichment like IOCs (threat intelligence). DL engines will therefore, identify malicious activity, In particular there are lots of benefits for large environments, since it is necessary to analyze only a smaller amount of data. These new safety models are cheaper than scaling DPI solutions and solves the problem of threats even in encrypted communication.
Intelligent Security Solutions
Artificial intelligence has been integrated into what is now called Intelligent Security Solutions; it is protocols, software or even raw code added to a company or institution’s IT system. AI then adds a new safety layer that can learn from threats, security violations and other collected data.
Intelligent Security Solutions are able to adapt to new threats and secure new types of applications by combining aspects of machine learning and artificial intelligence with traditional security applications. In principle, this system is based on AI algorithms which can learn from security breaches. As a result, the more attacks a system faces, better safety will be in the future to defend itself.
A solution called service resilience can show how AI detects a security breach and can even disable it. Daniel Miessler, Directory of Advisory Services from IOActive explains it as:
A big trend I see is a focus on service resilience, i.e., making it so that a DDoS can melt one provider or one datacenter, but your service will automatically migrate to another site that can serve the same content.
Additional solutions with AI : in addition to service resilience, include threats to several starter companies operating on such a line, for instance, Darktrace, Response automation, Fortinet, endpoint protection software with BioCatch or Centrify as its representatives, CrowdStrike or Risk-Based Authentication (RBA).
What is Blockchain
Blockchain technology is a decentralized ledger where anything once added in the ledger can be seen and verified by anyone and it can not be altered. Blockchain gave birth to cryptocurrency, where Bitcoin was the first of its kind. However, with technology gradually spreading worldwide, people in many industries started using it as means to increase cyber security. The decentralized ledger and its security aspect can be further explained as
Blockchain is distributed network with a million users worldwide, every user can add the information in the blockchain, and all blockchain data is tamper free. Each other member of the network shall check whether the data added to the blockchain is real. This can be accomplished using a three-key (private, public, and the receiver’s key) system, which enables members to verify the data veracity while also confirming its origin.
Blockchain technology is designed so that no central authority or storage facility can control it. Each network user plays an integral part in the blockchain’s storage. Everyone shall verify the stored and shared data to ensure that false data is not added or that existing data cannot be deleted.
How Blockchain is Secured
A hacker must destroy the data stored in the global network on every computer to destroy or corrupt a blockchain. It could be millions of computers and a copy of some or all the data could be stored. Without the hacker being able to bring down a whole network at the same time (which is almost impossible), undamaged computers also known as “nodes” would continue to check and store all the data on the network.
Bigger blockchain networks with more users are at less risk for hackers due to the higher hash rate required to bring down or add a false entry on the blockchain.
This complex structure offers the ability to store and share information online as securely as possible as we have seen with blockchain. For that reason, innovators have begun using this technology to prevent fraud and increase data protection in various sectors. Blockchain is still Hackable but it is something very difficult to achieve.
Guardtime has already succeeded in using blockchain technology to safeguard essential data. The company removes the need to check keys, all data pieces are distributed to nodes across the system. When someone tries to alter the data, the system analyzes the entire mass of chains, compares them and excludes any chains that does not validate with the nodes.
Using Blockchain to prevent DDoS Attacks
The implementation of blockchain technology would decentralize DNS, spread the content to many of nodes and prevent hackers from attacking. Only those who have domain editing rights (domain owners) would be granted, and no other user would be permitted to make changes which significantly lowers the risk of unauthorized parties being able to access or change data. A system can ensure it is invulnerable to hackers by using blockchain to protect data unless each node is attacked together with a very coordinated hack.
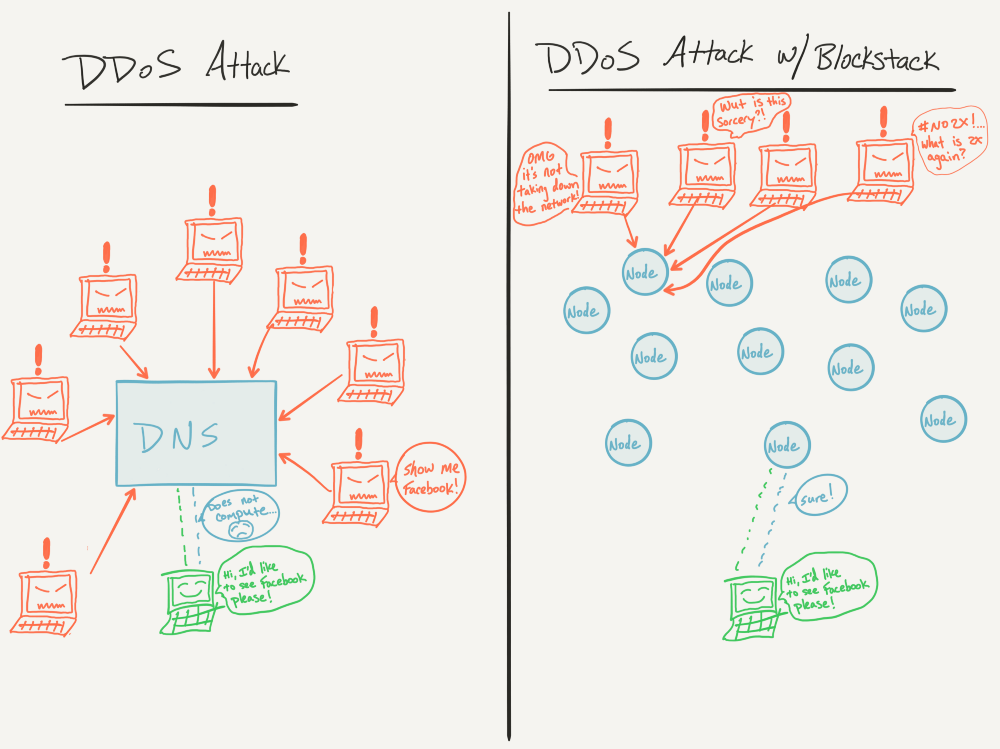

Individual companies in this field are already implementing blockchain to prevent DDoS attacks. Blockstack, for example, offers a completely decentralized DNS option. The company concept consists of decentralizing the entire global web through the removal of all third parties from web servers, ID systems, and databases.
MaidSafe is a similar UK based company. Their aim is also to decentralize the web and create a new Internet that allows users to run apps and store data in a safe environment while using the internet with no apparent change. Users can choose how much they wish to devote to the network by logging in for this service.
This system provides ‘safecoin’, a cryptocurrency, to offset the value the users provide. Each MaidSafe file is encrypted, fragmented and shared between users. The only person who can reread the data is the owner and makes sure nobody other than the authorized owner accesses the data.
Cybersecurity Using Blockchain Technology
To safely store millions of data on the platform, this distributed ledger is built and written using some architecture modifications. It is designed using its working protocol proof that every person belonging to the blockchain accounts for all the changes made so that all changes must be approved. Similarly, it permits a trustless principle in which all transactions are anonymous but remain on the chain and identification is stored keeping the integrity of data. In other words, blockchain is the next step in the development of databases.
Blockchain expert Dinis Guarda said
What is used to secure the authentication of the source of the transaction is cryptography, through the hash codes. There is never a duplicate recording of the same transaction. As such, the need for a central intermediary is not there anymore. This breaks with the paradigm of centralized consensus (when one central database is used to rule transaction validity).
Blockchain platforms are also used to validate any changes that can be made on any particular block with a request for users to prove ownership through a two type of consensus among all members called proof of stake. Proof of stake (PoS) is a way to achieve distributed consensus via a blockchain network. Proof of work (PoW), on the other hand, calls on users, for validating electronic transactions, to repeatedly perform hashing algorithms or other client puzzles. Both methods are deemed valid for the use of any modifications on the blockchain among all users. Hundreds, if not thousands, of users, will, therefore, keep the blockchain-Intruders free from any external changes.
However, the feature that most cyber security experts have looked at is the ability to develop smart contracts using a blockchain platform. Smart contracts not only define the rules and penalties for an agreement but also automatically enforce those obligations for all parts.
Instead of legal language, smart contract terms are recorded in a computer language. A suitable distributed ledger system can automatically execute smart contracts. The possible benefits of smart contracts include low contracting, enforcement, and compliance costs. Therefore, contracts for numerous low-value transactions are securely viable.
A company that raises a lot of money for its blockchain security platforms is NuCypher, Acronis, and the IBM blockchain platform or Facebook.
Merging AI and Blockchain
Both these technologies are contradictory and work on entirely different paradigms but combining them sounds promising. The companies now seek to develop business applications that connect AI and Blockchain in the real world. The main feature of blockchain is that it is secure, allowing AI code to be inserted into its platform is another feature which makes the merger feasible for organizations.
Artificial Intelligence and Blockchain
| Aspect | Artificial Intelligence | Blockchain |
| Nature | Centralized | Decentralized |
| Access | Closed | Open |
| Transparency | Black Box | Transparent |
| Approach | Probabilistic | Deterministic |
The two technologies are opposite but combining them will mark the beginning of a completely new paradigm.
It provides an additional guard against cyber attacks when AI and Blockchain are used together. AI can be trained to automate detection of real-time attack while blockchain is responsible for keeping integrity in decentralized databases.
Cyber Security for Defense


To receive 20% off the standard price of the conference, use code “25113.005_HACKOLOGY”.
One always wonders how interesting and useful a conference will be. To give you an idea, read Top Recommendations for Defending Against Cyber Threats which has been shared by the organizers. Once you are convinced it won’t be any issue to convince your boss.
Conclusion
The risk of being hacked increases as firms, governments and consumers rely on digital systems for their day-to-day activities. The more they adopt the technologies, the higher the risks they face. Additionally, new solutions to ease day-to-day businesses, such as Artificial Intelligence for Operational Systems and enormous IT databases create complexity.
However, these new technologies can also be their most reliable allies! They can provide new levels of protection that create a strong shield of protection against hackers if properly designed and integrated.
As the size and complexity of cyber attacks increase, artificial intelligence (AI) helps under-resourced security analysts stay ahead of threats. AI provides immediate insights to guide you through the noise of thousands of daily alerts and dramatically decreases response times by curating the intelligence of a threat from millions of research papers, blogs, and news stories.
All critical data such as identity, money and private information can be hacked, though the protection we provide to secure online data is weak and breakable. Blockchain and AI are born from past, predictive, reactive and validatory human behaviors that make them one of the most promising security measures.
The work together between Blockchain Technology and Artificial Intelligence remains unknown. Although both have a fair share in the intersection, it is still in the experimental phase but the potential and hopes are high












[…] happening on June 26 – 28, 2019 at Sheraton Pentagon City, Arlington, VA. I did cover about AI and Blockchain in Cybersecurity Threat Detection recently and how speakers in the same conference will present in depth analysis on these […]